About Lights
There are a variety of reasons why the lights in your house may not be working as expected. It may be that the light is not turning on, not turning off, not dimming, flickering, or needing frequent replacements. Electrical repairs should only be performed by a professional, but if you feel confident in your abilities and proper safety measures are taken, you should be able to complete minor electrical repairs yourself.
Common Types of Residential Bulbs
The three most common light technologies that you may find in your home are incandescent bulbs, fluorescent bulbs, and LED bulbs.
Incandescent bulbs use electricity to burn a filament inside a vacuum sealed bulb to produce light.
Incandescent bulbs were first produced in 1879 and the last major advancement in this technology was the introduction of tungsten filament in 1910 which is still being used today. Using 110-year-old technology in our modern homes has its drawbacks which primarily consist of short bulb life, wasted energy, and potentially fire causing levels of heat. Incandescent bulbs are inefficient which means that the bulb converts a small amount electricity (10%) into light, and the rest of the electricity (90%) is wasted as heat.
Fluorescent bulbs use electricity to heat mercury, which is a toxic metal, to the point that the mercury becomes a gas which causes the release of invisible photons that only become visible when they hit the phosphor powder inside the glass bulb.
Fluorescent bulbs were a huge improvement to incandescent bulbs because they converted more than half of the electricity into light. Fluorescent bulbs were invented in 1926 and remained unchanged until Compact Fluorescent (CFL) bulbs were invented in 1976.
Unfortunately, CFL bulbs had the same health hazards as traditional fluorescent bulbs since they also relied on the toxic metal mercury. In 2002 CFLs had their last big sales surge using clever marketing claims that touted CFLs as being the most energy efficient bulb available. The claims of energy efficiency were found to be bogus since they didn’t report on the substantial amount of energy wasted during the bulb’s initial warmup period which took 3 minutes every time the light was turned on. The health hazards, energy inefficiencies and mediocre performance of CFLs resulted in them being outsold by LED lights
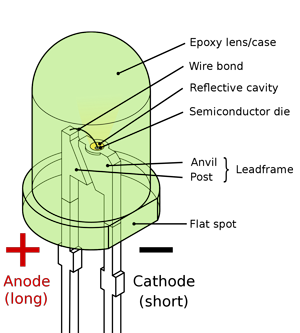
LED bulbs use an energy efficient Light Emitting Diode (LED) that produces light when electricity is passed through a semiconducting material known as the diode.
LEDs were developed in 1962 and became an affordable lighting solution for home illumination in 2011. LEDs convert a significant amount of electricity (>80%) into light and hardly any electricity into wasted heat. LEDs are non-toxic and are now able to be produced at a lower cost than incandescent bulbs.
LEDs are used in most modern lighting applications from holiday lights to vehicle headlights. The transition to LED technology in the home had a significant impact on the run times of air conditioners since they no longer had to offset heat produced by incandescent bulbs. LED Christmas lights have reduced the number of indoor tree fires because they don’t produce as much heat as traditional incandescent string lights.
Bulb Issues
If a light bulb isn’t turning on when requested at the switch the first diagnostic step should be to replace the light bulb. If the new bulb works then the issue has been resolved.
Incandescent bulbs can burn out the filament or the filament can break if the bulb was dropped or subjected to vibration. When installing light bulbs, the oils from our hands can stay on the bulb and high heat lights such as halogen bulbs can crack when the oils get superheated resulting in hot spots on the glass.
Fluorescent bulbs can also overheat which may weaken the seal on the ends of the bulb. A seal failure can release gaseous mercury into the room thus making the bulb inoperable. A ballast is used to supply a high voltage of electricity to cold start the light bulb when it is first turned on. Ballasts often go bad and need replaced. If there is an issue with the ballast or the mercury gas inside the bulb it is common to see the light bulb flicker before complete failure.
LED bulbs do produce heat, but they produce significantly less heat than the competition. However, heat can kill LED bulbs if the diode or controller circuitry is over heated. Using the appropriately sized bulb for the fixture that is housing the bulb will reduce the likelihood of a failure.
Switch Issues
The first place to check for an electrical issue is the switch. Sometimes the switch may not fully be in the on or off position, and when the light is being controlled by a 3-way switch this can prevent the light from turning on. It is possible for a mechanical switch to fail, but the types of switches that fail most often are dimmers and smart switches.
Dimmers work in one of two ways. Dimmers either reduce the voltage through Constant Current Reduction (CCR) which converts the excess electricity into heat or through Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) which quickly turns the power to the light on and off.
Backwards compatible dimmable LED bulbs will often have an integrated PWM circuit that interprets the drop in voltage from a CCR. The lightbulb that you installed may not work properly or at all depending on the type of dimmer that was installed and the bulb that is being used. Diagnosing this issue may take a little effort to figure out if it is an issue with the bulb or the dimmer.
Smart switches may need to be configured to work properly. There can be a primary switch that is directly connected to the circuit and a secondary switch that does not control the circuit but instead sends requests to the primary switch. Depending on the design of the home automation system, this repair may require a professional.
If the switch is connected to a timer, light sensor, or motion sensor the light may not turn on. Light and motion sensors sometimes will have a test mode, otherwise the required conditions must be met before the internal relay will close the circuit. Timers can be mechanical or electronic and testing them should be straight forward.
Circuit Issues
If there is an issue with the electrical circuit the light will not be able to turn on. These issues may include a tripped breaker, GFCI, AFCI, or damaged electrical components. Circuit breakers can be checked by the homeowner at the service panel. Circuit breakers can be traditional breakers, GFCI breakers, or AFCI breakers. If a breaker, GFCI, or AFCI immediately trips after being reset, the circuit should be left in the disconnected position and an electrician should be consulted because there is a problem with the circuit or the circuit breaker which could result in injury or damage to property.
Light circuits can be connected to GFCI receptacles. This practice is often found in bathrooms and garages. If the receptacle is tripped the lights in the room may not work. Resetting the GFCI should solve the issue, but it is possible that the GFCI receptacle is defective. Many GFCI receptacles are designed to stay disconnected if the device is not working as intended.
If a wire in the wall has been damaged by a nail, screw, drill, or any other type of mechanical action the light may not be able to turn on. If this is the case the power should be shut off and electrician should inspect and repair the circuit prior to turning the power back on.
When repairs are made in seemingly unrelated areas of the house such as replacing a switch or receptacle it is possible that a light circuit in a different room could be affected if the repair is not done properly.
Conclusion
Issues with light bulbs are common, but if you are buying the house and have not taken ownership of the house, you should inquire with the seller to learn what you can about the house or negotiate to have them repair the light. If the seller is unable or unwilling to repair the light, the above listed steps should help you diagnose the issue and figure out when you can do the repair yourself or when an electrician might be needed to make a repair.